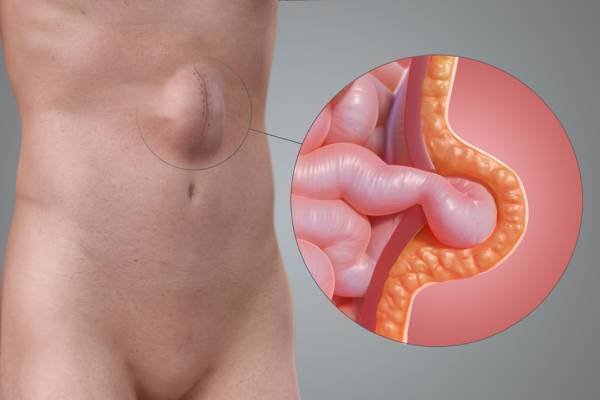
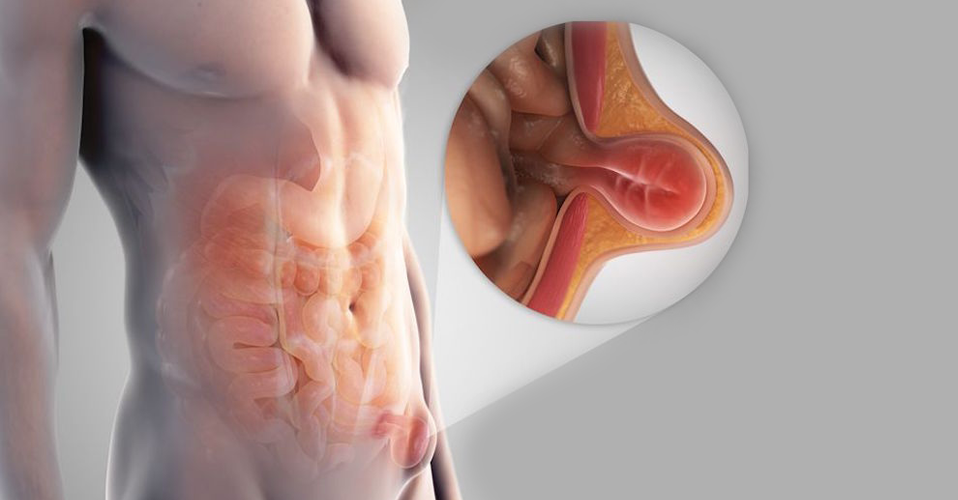
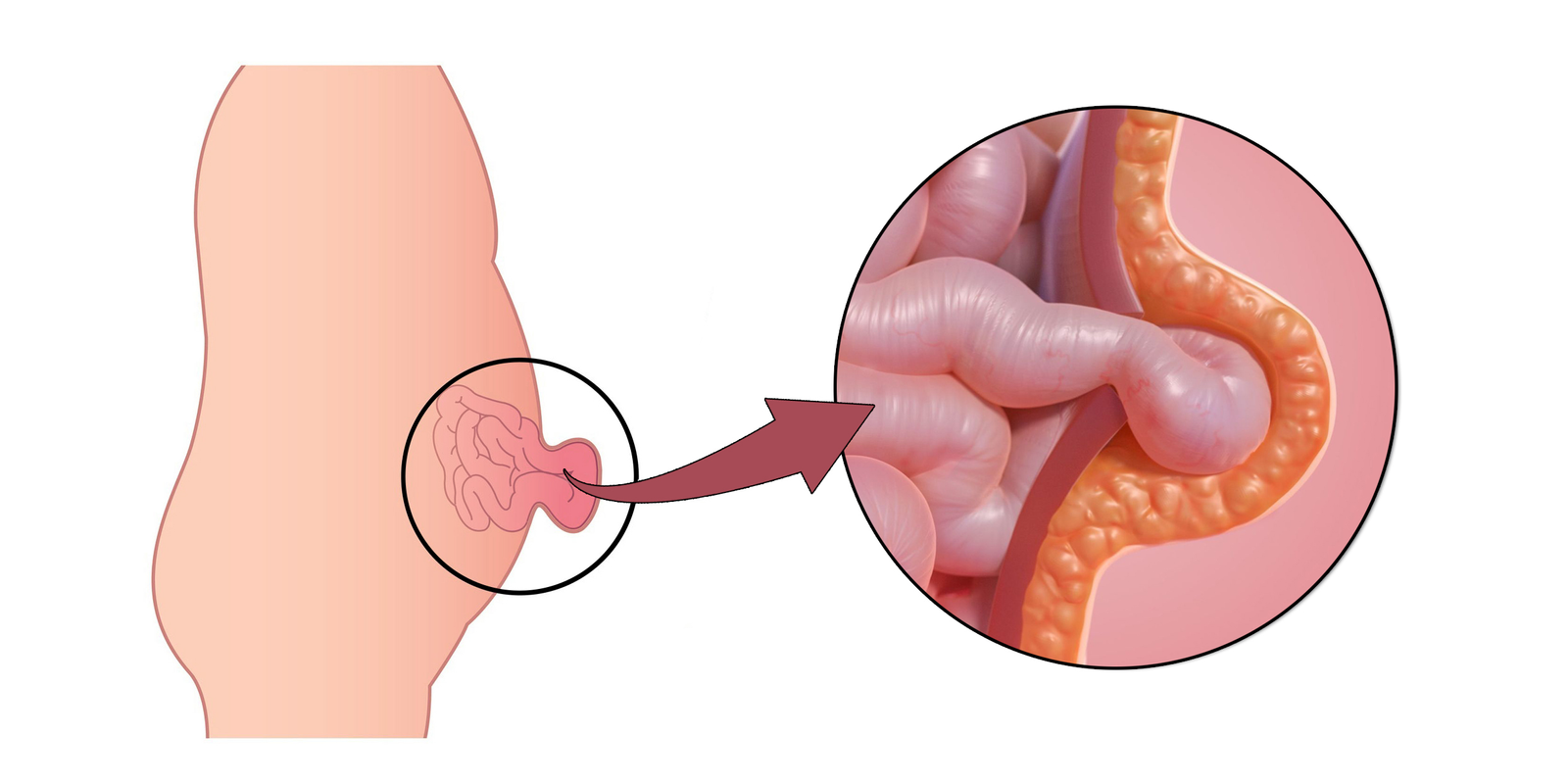
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, is a surgical technique used to perform procedures within the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions and specialized instruments. Unlike traditional open surgery, which requires a large incision to access the surgical area, laparoscopic surgery involves making several small incisions (usually between 0.5 to 1.5 centimeters in length) through which a laparoscope and other surgical instruments are inserted.
The laparoscope is a thin, flexible tube equipped with a high-resolution camera and a light source at its tip. It allows the surgeon to visualize the internal organs in real-time by projecting images onto a monitor. Additional instruments, such as graspers, scissors, and cautery devices, are inserted through separate incisions to perform the surgical procedure.
Laparoscopy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
Minimized Trauma: Laparoscopic procedures require smaller incisions, resulting in reduced trauma to the surrounding tissues and muscles. This often leads to less postoperative pain, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays compared to open surgery.
Improved Cosmesis: The smaller incisions used in laparoscopy result in minimal scarring, which is cosmetically more appealing to patients, particularly in areas such as the abdomen.
Reduced Blood Loss: The precision of laparoscopic instruments and the use of magnified images help minimize blood loss during surgery, reducing the need for blood transfusions.
Quicker Return to Normal Activities: Patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery typically experience a quicker recovery and can resume normal activities sooner compared to those undergoing open surgery.
Lower Risk of Infection: With smaller incisions and reduced exposure of internal organs to external contaminants, laparoscopic surgery carries a lower risk of surgical site infections.
Laparoscopy is used in various surgical procedures across different medical specialties, including gynecology, general surgery, urology, and gastroenterology. Common gynecological procedures performed laparoscopically include: