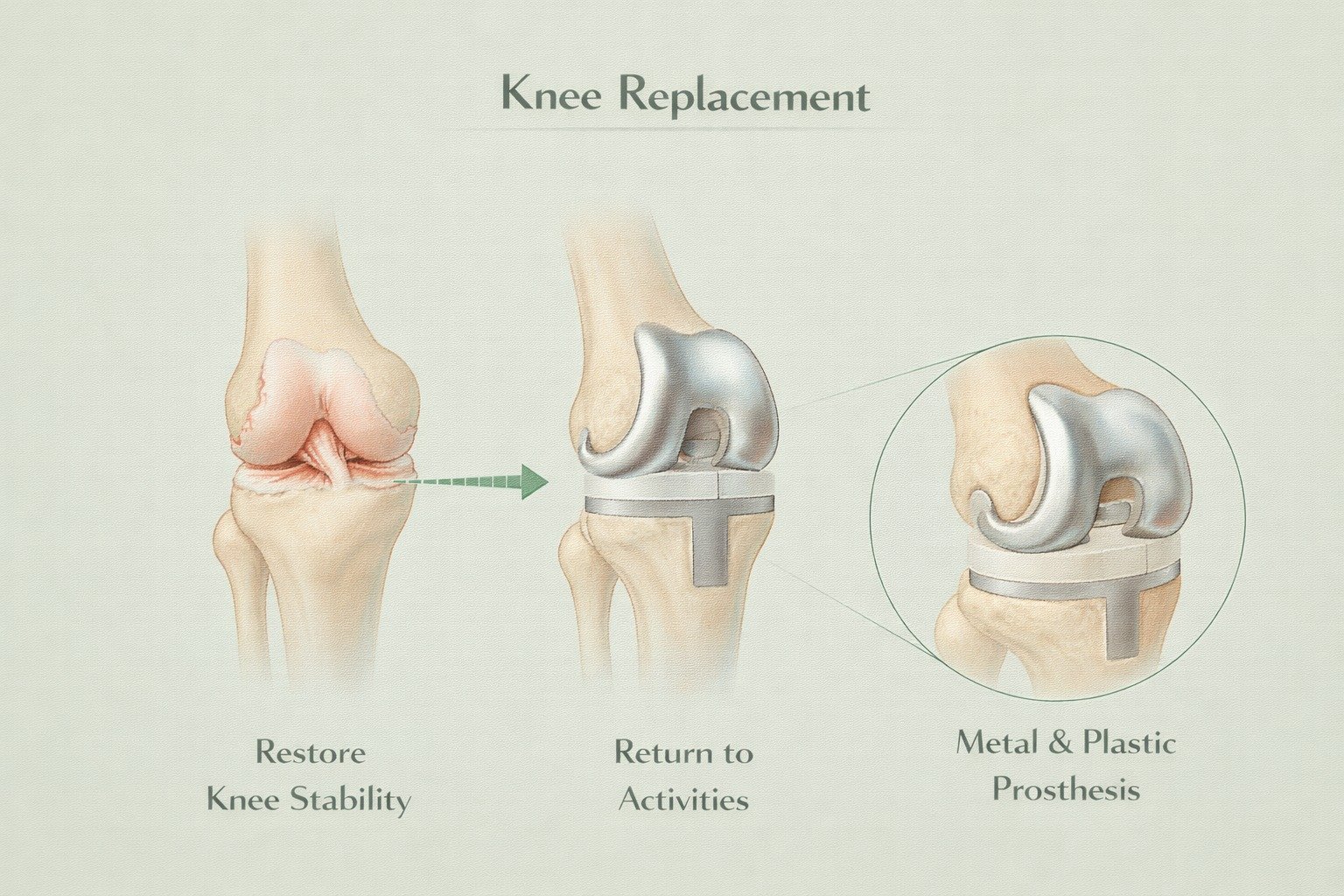
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is a procedure to replace a damaged knee joint with a prosthetic implant. It is recommended when severe knee damage causes chronic pain, limited mobility, and disability that cannot be managed by medications, physical therapy, or other conservative treatments.
The most common cause is advanced osteoarthritis, where the protective cartilage wears away, resulting in bone-on-bone friction.
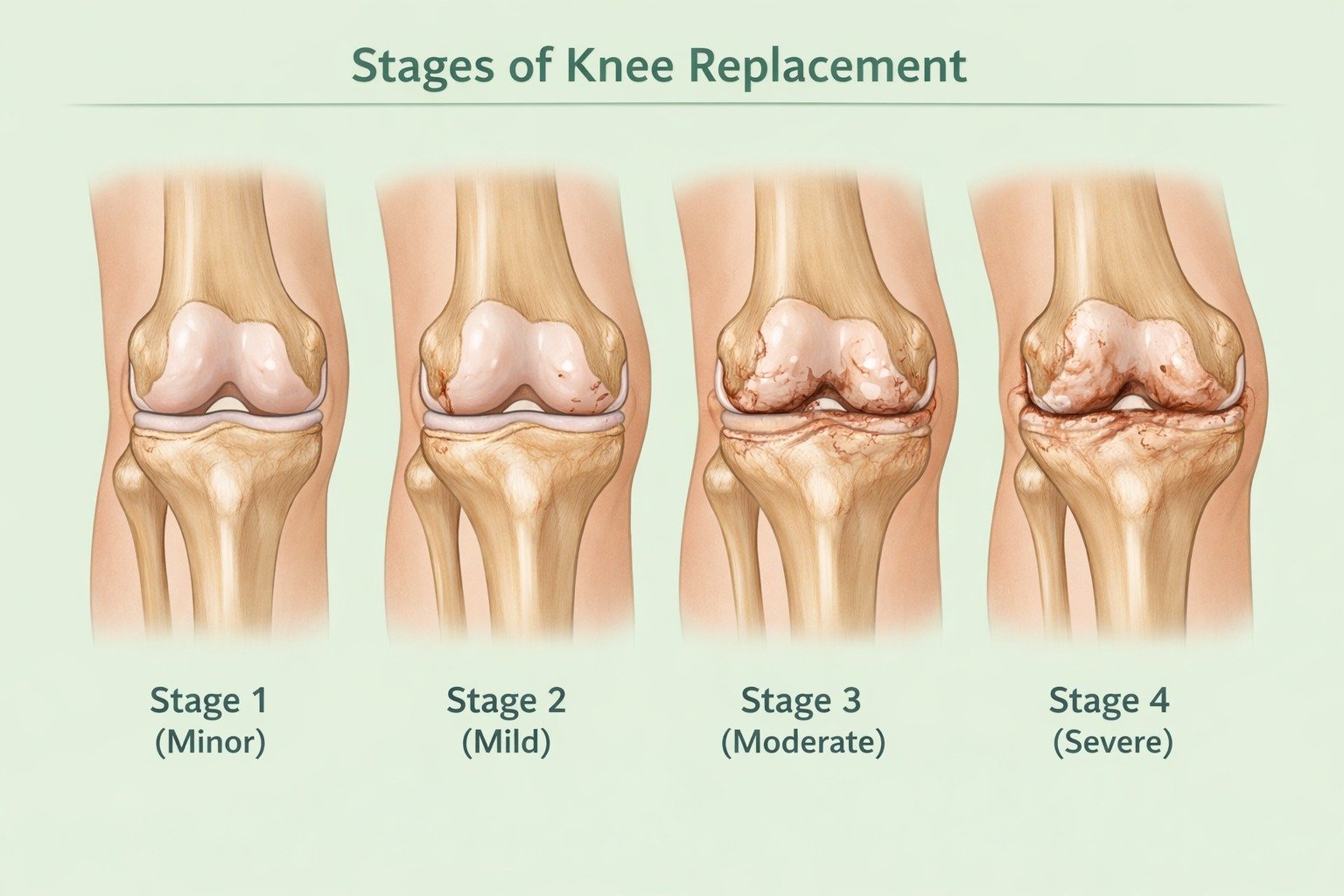
Stages of Knee Arthritis
Stage 1 (Minor): Minimal cartilage damage, usually no pain
Stage 2 (Mild): Bone spurs form, mild pain, cartilage thinning begins
Stage 3 (Moderate): Significant cartilage loss, frequent pain, stiffness
Stage 4 (Severe): Bone-on-bone contact, severe chronic pain, limited mobility; surgery typically recommended
The most common cause is advanced osteoarthritis, where the protective cartilage wears away, resulting in bone-on-bone friction.
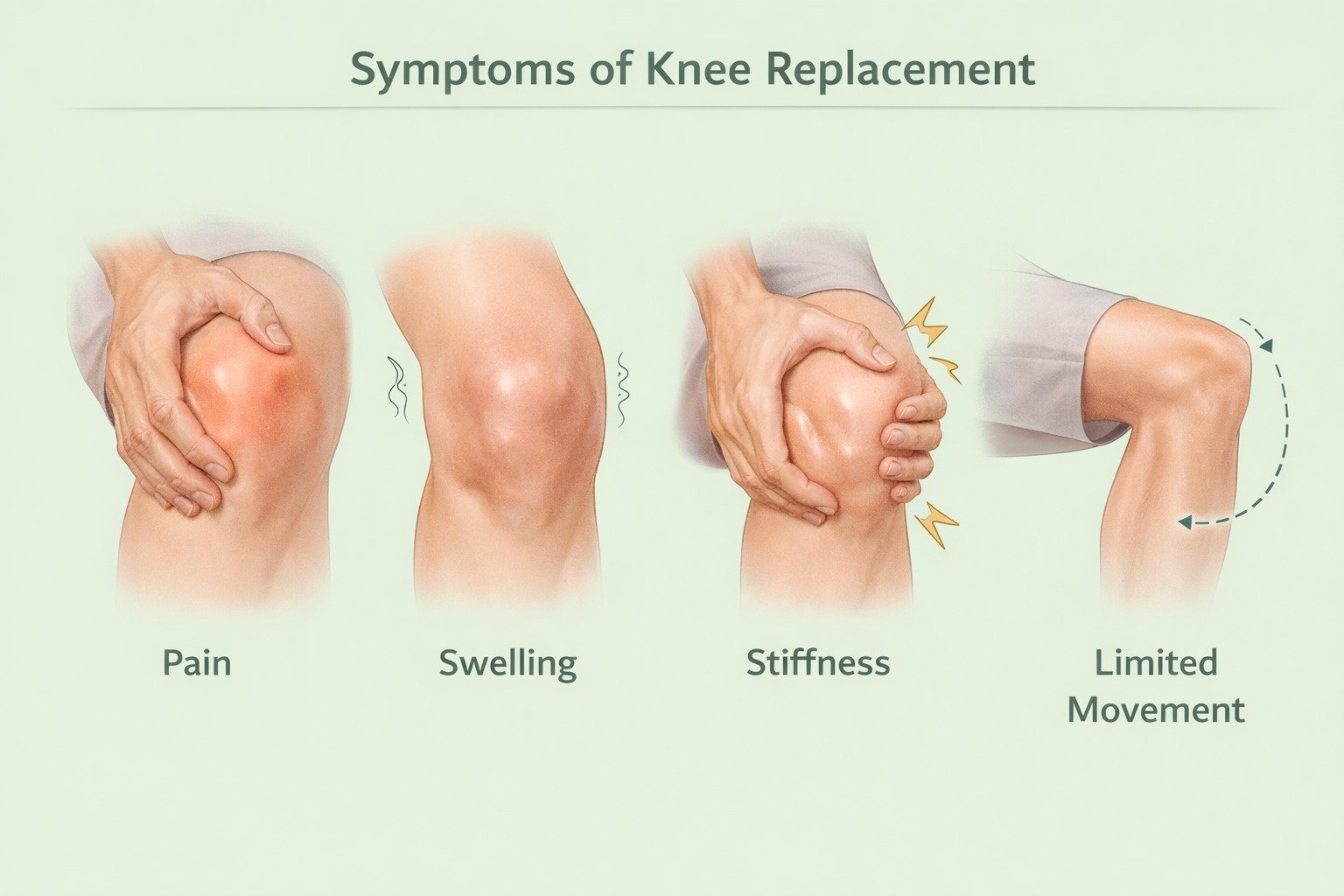
Symptoms Indicating Knee Replacement
Severe knee pain that persists even at rest or at night
Chronic swelling and inflammation not relieved by medications
Stiffness limiting bending or straightening of the knee
Knee deformity (bowing) or instability
Difficulty walking, climbing stairs, or performing daily activities
Failure of conservative treatments to relieve pain
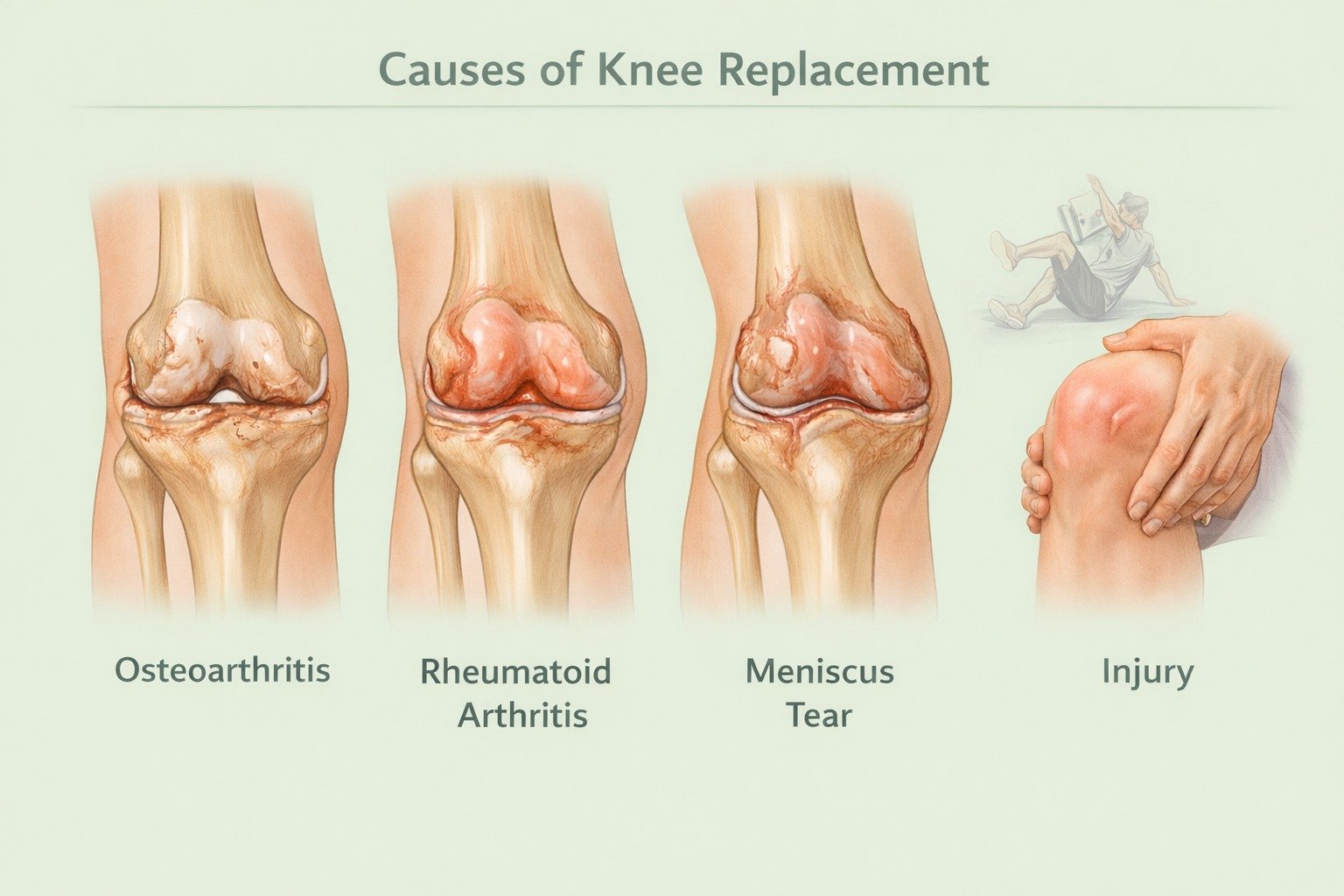
Causes & Conditions Leading to Knee Replacement
Osteoarthritis: Wear-and-tear degeneration of cartilage
Rheumatoid arthritis: Chronic joint inflammation
Post-traumatic arthritis: Following fractures or injuries
Avascular necrosis: Bone death from poor blood supply
Previous knee injuries, ligament or cartilage damage
Congenital or acquired bone deformities
Failed prior knee surgery
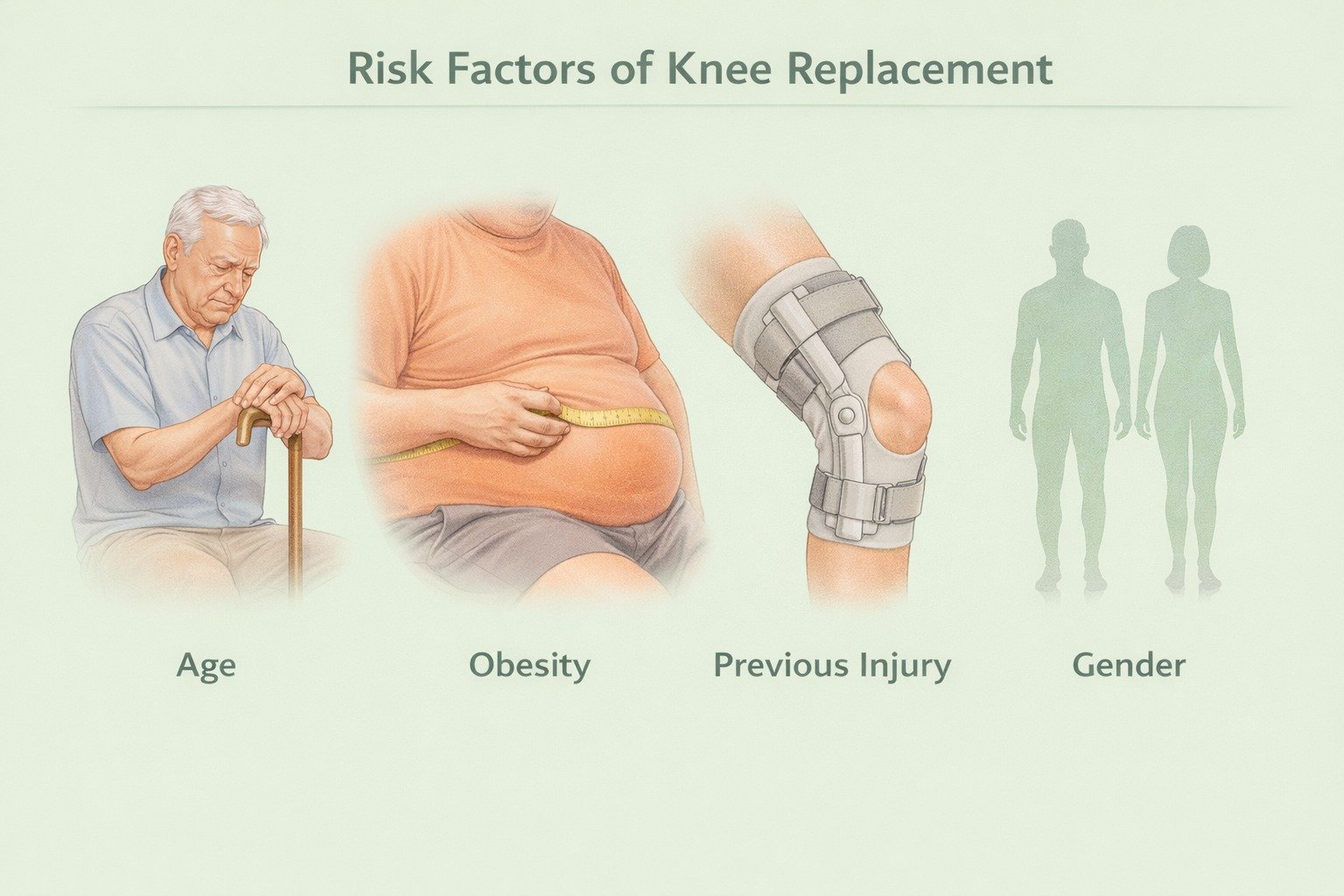
Risk Factors
Age over 50 (younger individuals may require replacement in severe cases)
Obesity (extra weight increases knee pressure)
Previous knee injury or surgery
Family history of arthritis
Occupations requiring frequent kneeling, squatting, or heavy lifting
High-impact sports
Genetic predisposition
Slightly higher risk in women
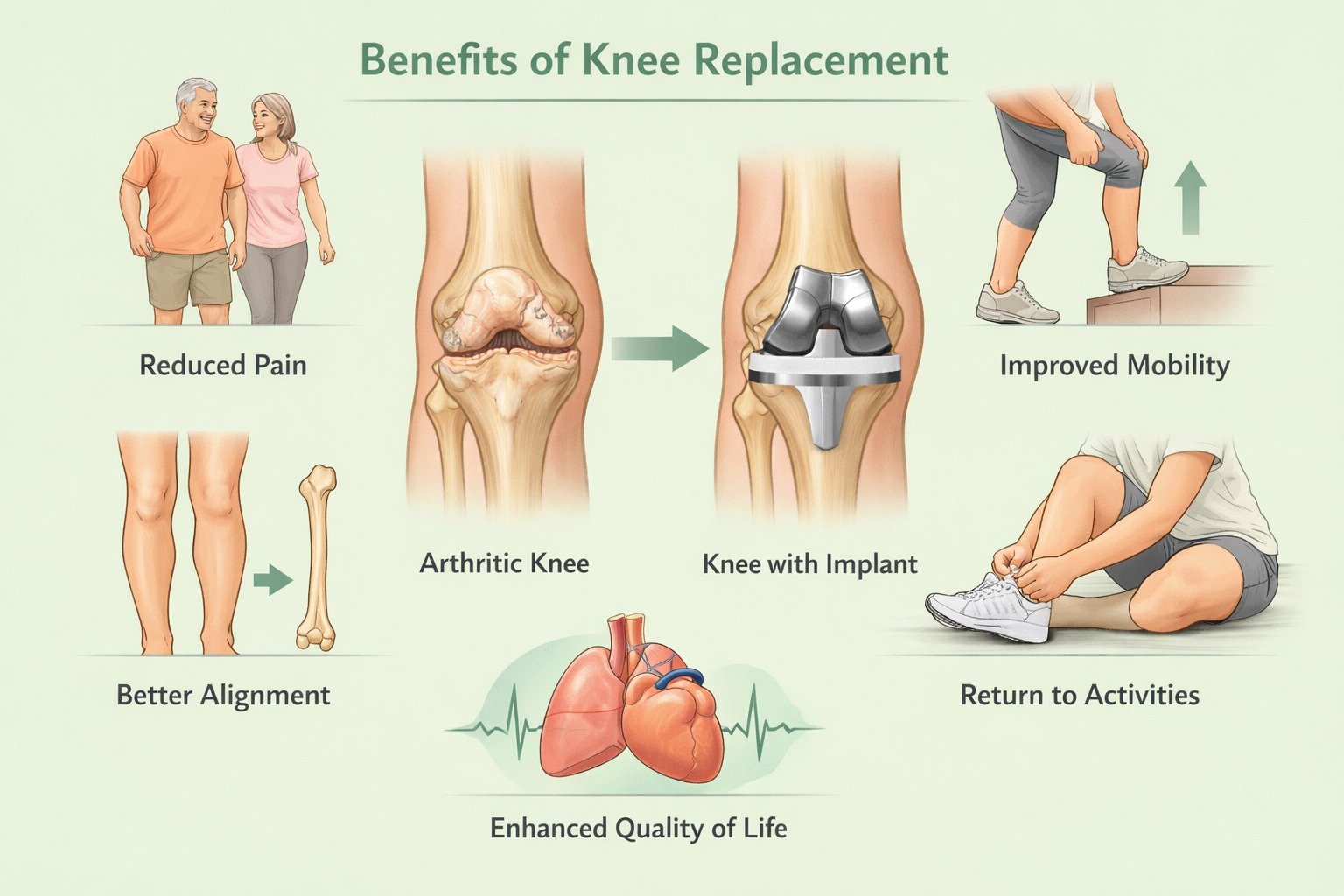
Benefits of Knee Replacement Surgery
Eliminates chronic knee pain – Relieves severe, bone-on-bone pain, nighttime discomfort, and reduces dependence on pain medications.
Restores mobility and daily function – Improves walking, stair climbing, standing from chairs, and overall gait and posture.
Significantly improves quality of life – Restores independence, boosts confidence, and reduces anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
Long-lasting and highly successful solution – Modern implants last 15–20+ years with a 90–95% success rate.
Enables an active, healthy lifestyle – Supports low-impact exercises, hobbies, travel, and social activities.
Corrects deformity and supports healthy aging – Fixes bow-legged or knock-knee alignment, reduces fall risk, and protects other joints
When to See a Doctor
Consult an orthopedic surgeon if:
Knee pain limits daily life
Pain persists despite medications or therapy
Conservative treatments fail
Pain affects sleep
Daily activities are difficult
Knee deformity worsens
Decision for knee replacement involves X-rays, physical examination, and symptom evaluation. Surgery is considered when other options fail, providing substantial pain relief and improved mobility.

