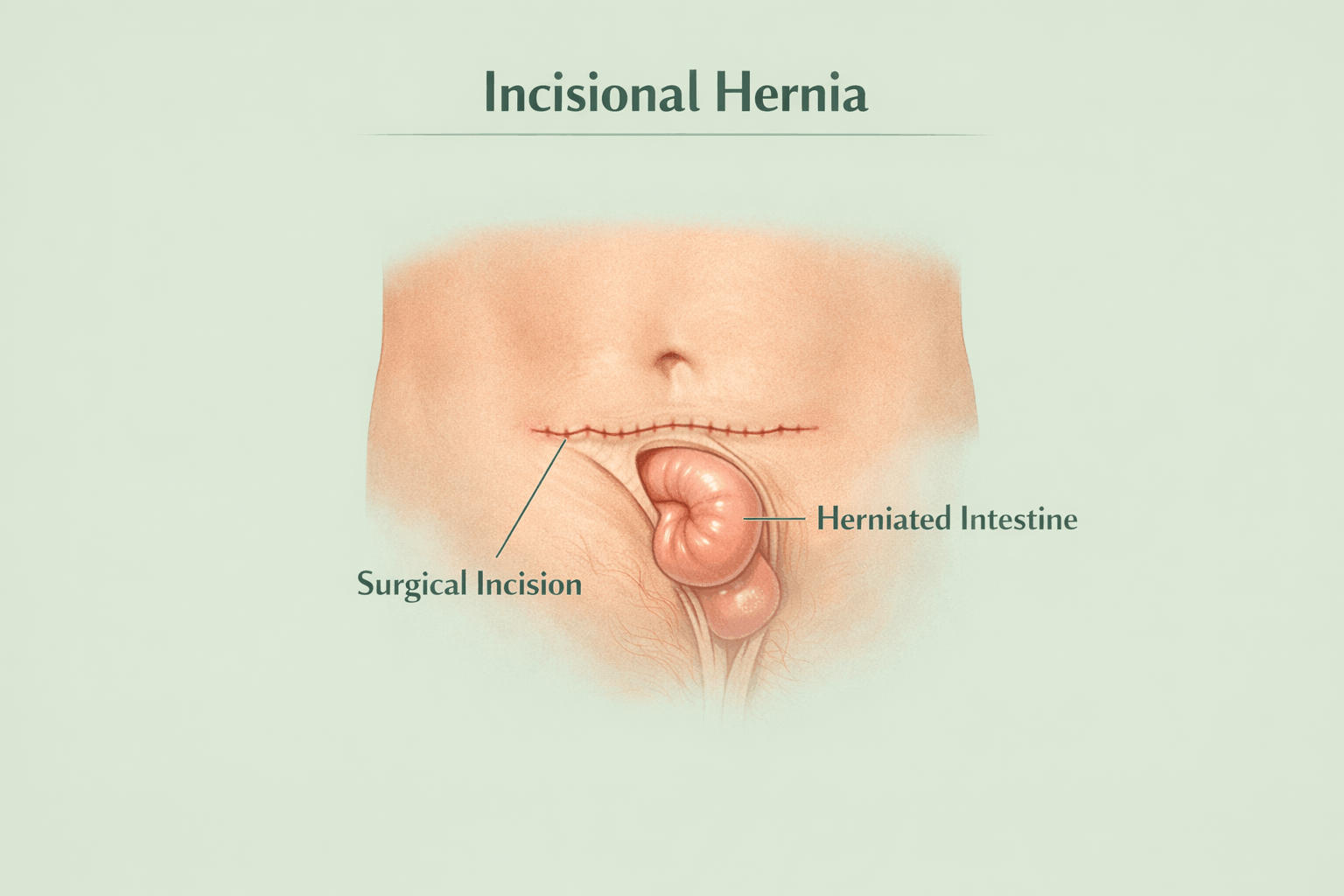
What Is an Incisional Hernia?
An incisional hernia is a condition that develops at the site of a previous abdominal surgery. It happens when the muscles and tissues of the abdominal wall do not heal completely after surgery. Because of this weakness, part of the intestine or internal tissue can push through the scar, causing a visible bulge.
This type of hernia can appear weeks, months, or even years after surgery.
Common Symptoms of Incisional Hernia
A bulge or swelling near a previous surgical scar- Pain or discomfort, especially when coughing, lifting, or straining
- Burning or aching sensation at the site
- Feeling of heaviness or pressure in the abdomen
- Bulge becomes larger when standing and smaller when lying down
- Nausea or vomiting (in severe cases)
- Constipation or difficulty passing gas
What Causes an Incisional Hernia?
- A bulge or swelling near a previous surgical scar
- Pain or discomfort, especially when coughing, lifting, or straining
- Burning or aching sensation at the site
- Feeling of heaviness or pressure in the abdomen
- Bulge becomes larger when standing and smaller when lying down
- Nausea or vomiting (in severe cases)
- Constipation or difficulty passing gas
Risk Factors
You may have a higher risk if you have:
A history of abdominal surgery (especially emergency surgery)
Obesity or excess body weight
Diabetes or poor wound healing
Smoking habits
Chronic cough or lung disease
Pregnancy soon after surgery
Age above 60 years
Poor nutrition or low protein levels
Long-term steroid use or weak immunity

Benefits of Incisional Hernia Surgery
Prevents life-threatening complications – Eliminates the risk of strangulation, bowel blockage, and tissue damage.
Avoids emergency surgery – Timely treatment reduces urgent, high-risk surgical situations.
Relieves chronic pain and discomfort – Removes pressure, heaviness, and allows pain-free movement.
Restores abdominal wall strength – Improves core stability and supports normal physical function
Improves daily activity and mobility – Makes bending, lifting, walking, and returning to work easier.
Improves confidence and peace of mind – Reduces anxiety, enhances body image, and improves overall quality of life.
Surgical Treatment Options
Open Surgery
Laparoscopic (Keyhole) Surgery
Robotic Surgery
Most repairs use mesh reinforcement to reduce recurrence and provide long-lasting results. Your surgeon will choose the best option based on hernia size and health condition.

When Should You See a Doctor?
Seek emergency medical care if you experience:
Sudden, severe abdominal pain
Nausea or vomiting with a painful bulge
Hernia that becomes hard, tender, or painful
Red, purple, or dark skin over the bulge
Fever along with hernia symptoms
Inability to pass stool or gas
Consult a doctor if:
You notice a new bulge near a surgical scar
Pain or swelling is increasing
Daily activities become uncomfortable
Early treatment helps prevent serious complications.

