What is an ACL Injury?
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the key ligaments that stabilize the knee joint. It connects the thighbone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia) and controls forward movement and rotation of the shinbone.
ACL injuries are among the most common knee injuries, especially in athletes involved in high-demand sports. Injuries can range from a mild sprain to a complete ligament tear.
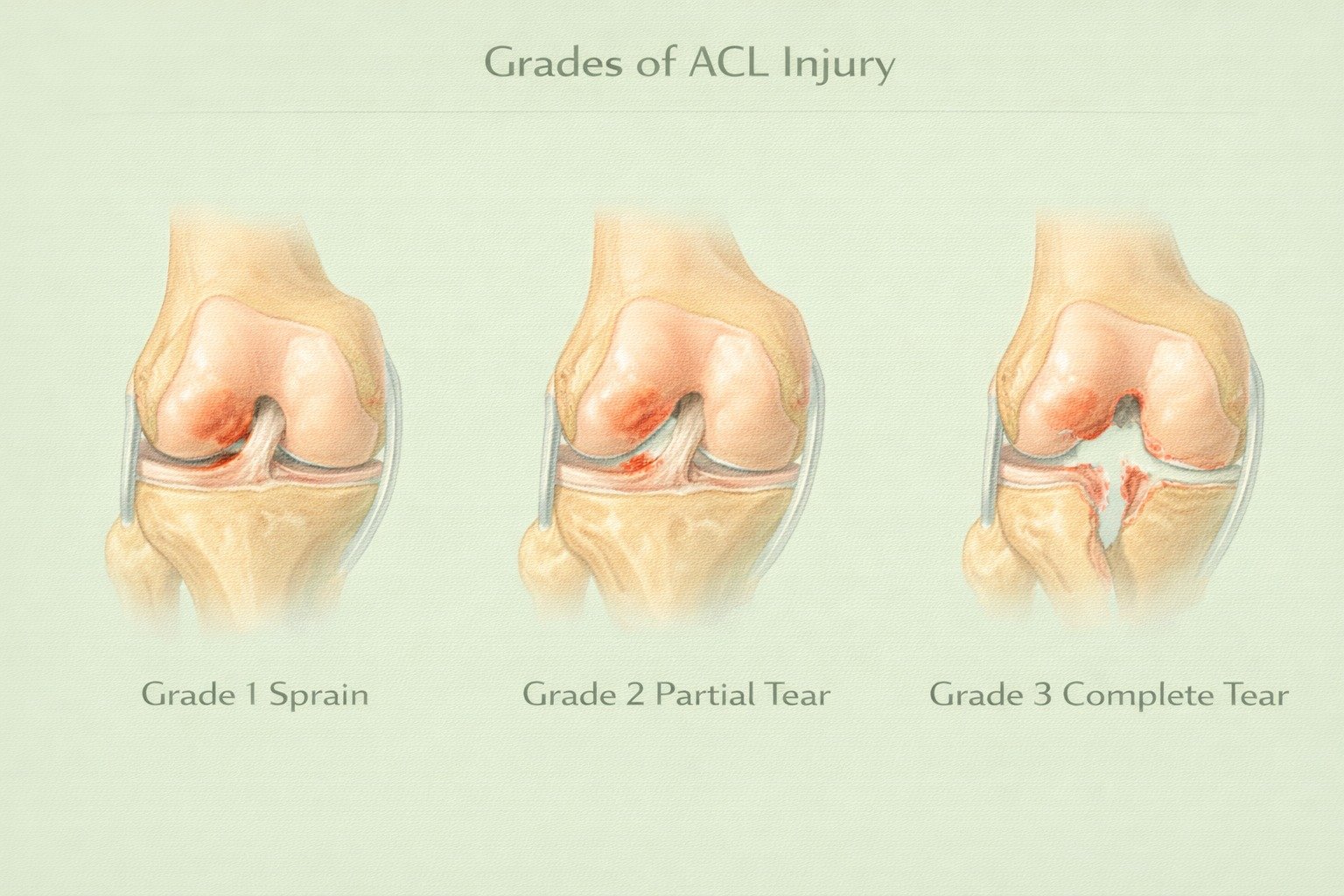
Grades of ACL Injury
Grade 1 (Mild Sprain): Ligament stretched but intact; knee remains stable.
Grade 2 (Partial Tear): Ligament partially torn; mild instability may occur.
Grade 3 (Complete Tear): Ligament completely torn; knee is unstable; usually requires surgery.
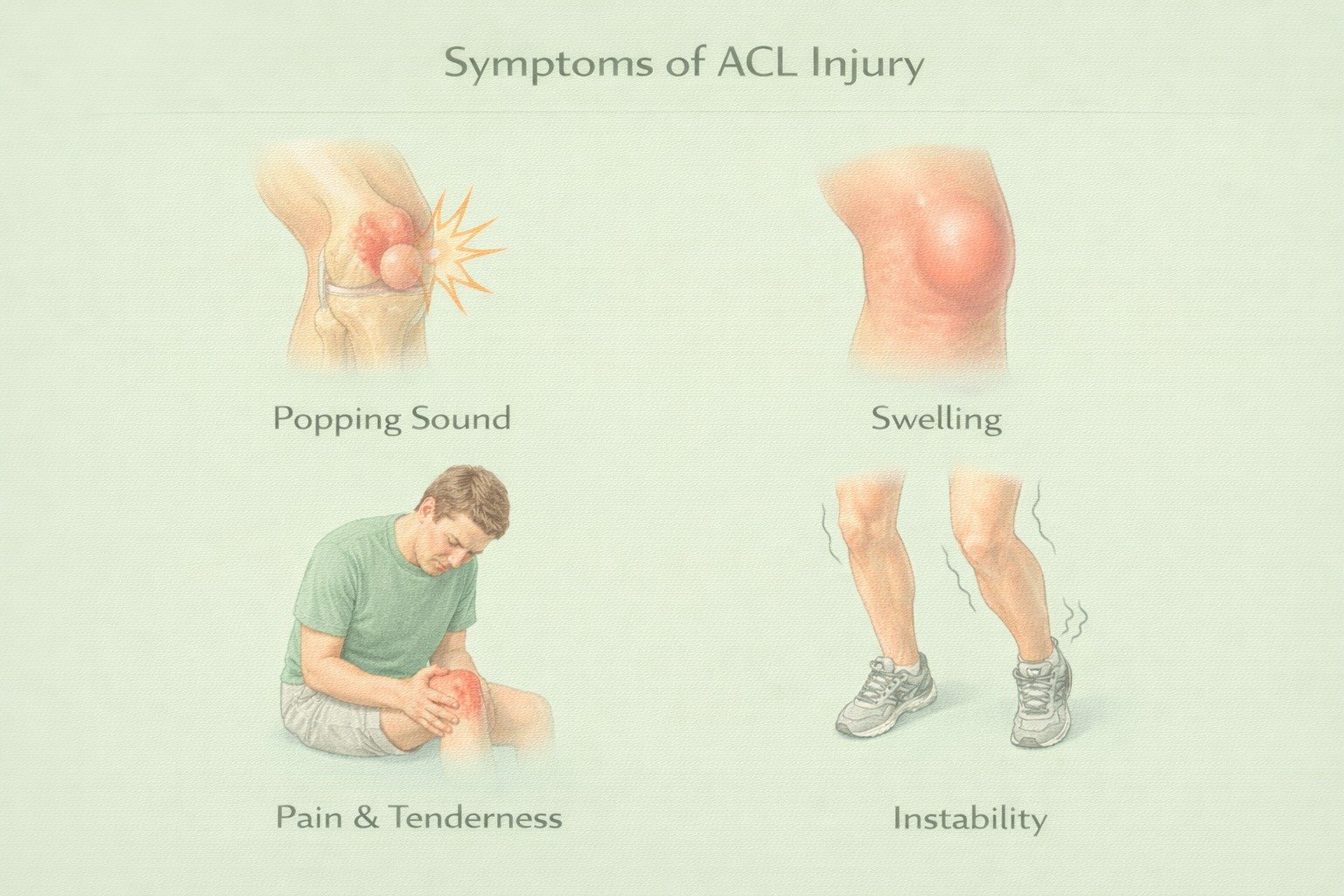
Symptoms of ACL Injury
Loud "pop" or snapping at the time of injury
Severe knee pain and inability to continue activity
Rapid swelling within hours
Loss of range of motion
Feeling of instability or knee “giving way”
Tenderness along the joint line
Difficulty walking or bearing weight on the injured leg
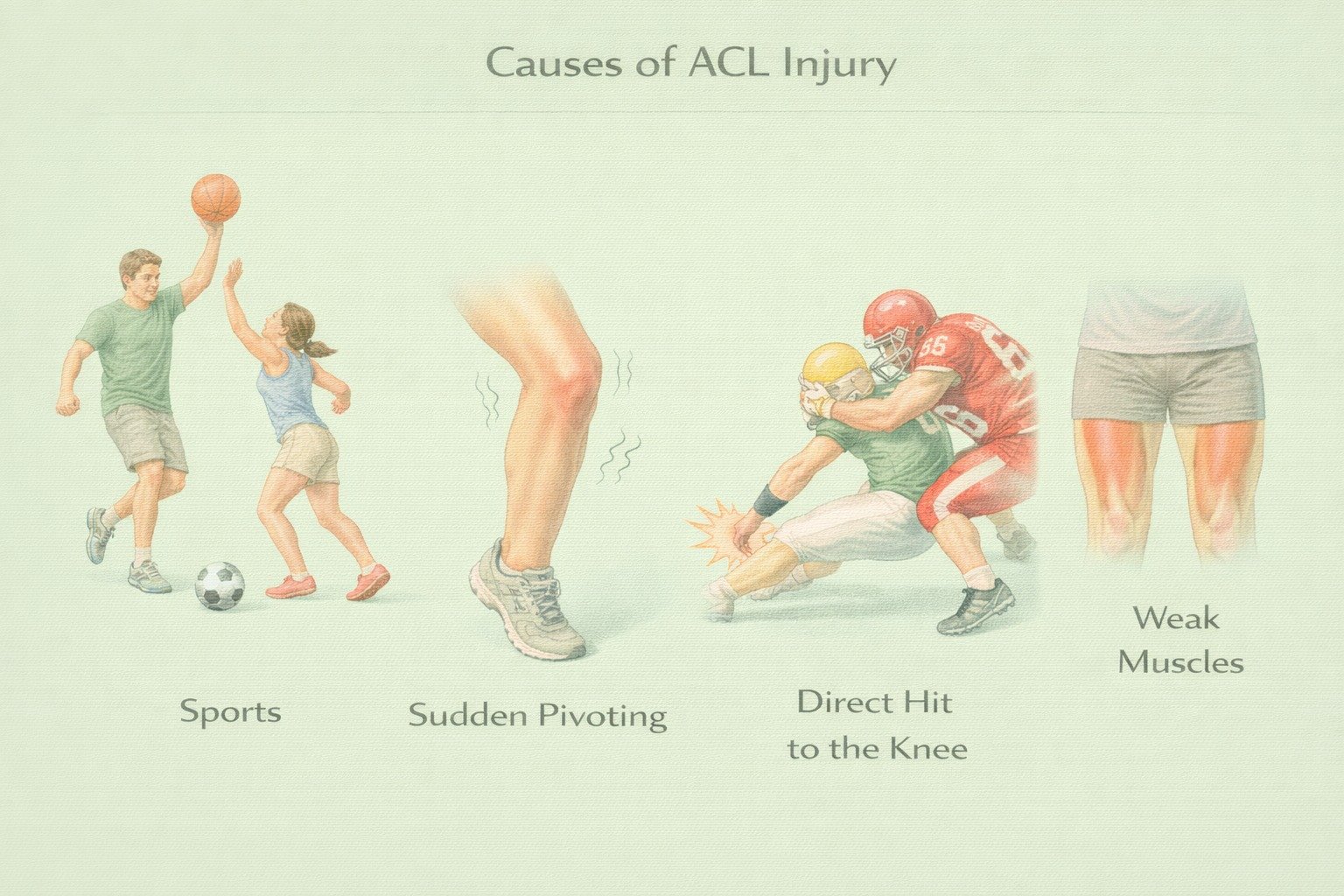
Causes of ACL Injuries
Sudden stops or changes in direction while running
Pivoting with foot planted
Landing awkwardly from a jump
Direct blow or collision (less common)
Hyperextension of the knee
Non-contact injuries are most common in sports
Risk Factors
High-risk sports: soccer, basketball, football, skiing, gymnastics
Female athletes (2–8 times higher risk)
Muscle imbalances or poor conditioning
Previous ACL injury
Narrow intercondylar notch (anatomical factor)
Improper footwear or playing surface
Neuromuscular control deficits

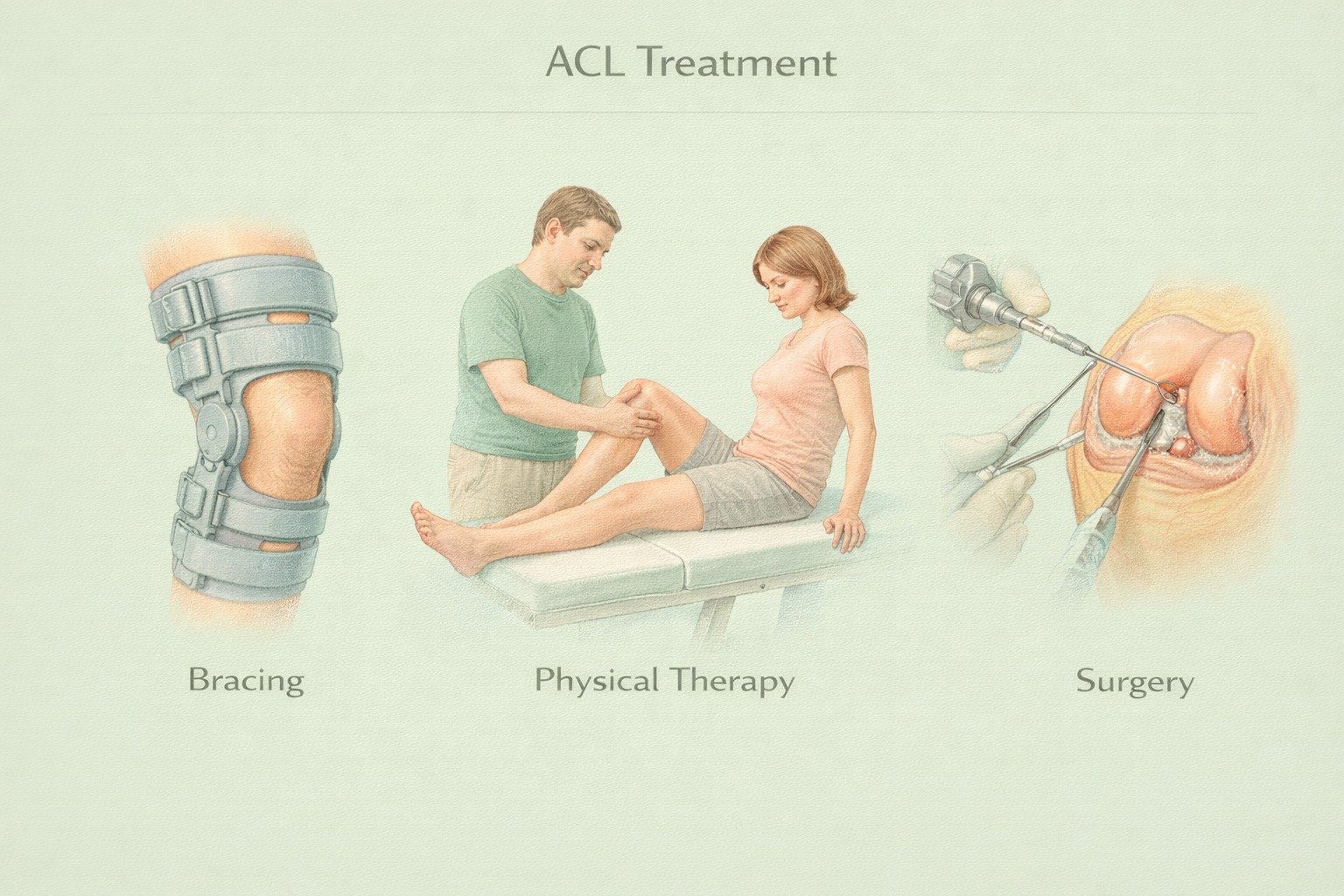
ACL Treatment Options & Benefits
Arthroscopic surgery: minimally invasive, small incisions, faster recovery
Graft options:
Patellar tendon graft (strong, gold standard)
Hamstring tendon graft (less anterior knee pain)
Quadriceps tendon graft (good for revisions)
Allograft (no harvest site, faster surgery)
Surgeon tailors graft type to patient needs

Surgical Techniques & Graft Options
Arthroscopic surgery: minimally invasive, small incisions, faster recovery
Graft options:
Patellar tendon graft (strong, gold standard)
Hamstring tendon graft (less anterior knee pain)
Quadriceps tendon graft (good for revisions)
Allograft (no harvest site, faster surgery)
Surgeon tailors graft type to patient needs

When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical care if:
Knee “pops” and gives out
Severe pain or swelling occurs
Cannot bear weight on the leg
Knee feels unstable
Seek immediate medical attention if you hear a pop and feel your knee give out, experience severe pain and swelling, cannot bear weight on the leg, feel the knee is unstable, or notice immediate swelling after injury. Early diagnosis through physical examination and MRI imaging is crucial. Treatment depends on injury severity and activity level, ranging from physical therapy for partial tears to surgical reconstruction for complete tears, especially in active individuals. Rehabilitation is essential regardless of treatment approach to restore strength, stability, and function.

